What is CMM (SEI Capability Maturity Model)?
According to the Carnegie Mellon University Software Engineering Institute, CMM is a common-sense application of software or business process management and quality improvement concepts to software development and maintenance. Its a community-developed guide for evolving towards a culture of engineering excellence, model for organizational improvement. The underlying structure for reliable and consistent software process assessments and software capability evaluations.
The Capability Maturity Model for Software (CMM) is a framework that describes the key elements of an effective software process. There are CMMs for non software processes as well, such as Business Process Management (BPM). The CMM describes an evolutionary improvement path from an ad hoc, immature process to a mature, disciplined process. The CMM covers practices for planning, engineering, and managing software development and maintenance. When followed, these key practices improve the ability of organizations to meet goals for cost, schedule, functionality, and product quality. The CMM establishes a yardstick against which it is possible to judge, in a repeatable way, the maturity of an organization's software process and compare it to the state of the practice of the industry. The CMM can also be used by an organization to plan improvements to its software process. It also reflects the needs of individuals performing software process, improvement, software process assessments, or software capability evaluations; is documented; and is publicly available.
The Five Maturity Levels described by the Capability Maturity Model can be characterized as per their primary process changes made at each level as follows:
1) Initial The software process is characterized as ad hoc, and occasionally even chaotic. Few processes are defined, and success depends on individual effort and heroics.
2) Repeatable Basic project management processes are established to track cost, schedule, and functionality. The necessary process discipline is in place to repeat earlier successes on projects with similar applications.
3) Defined The software process for both management and engineering activities is documented, standardized, and integrated into a standard software process for the organization. All projects use an approved, tailored version of the organization's standard software process for developing and maintaining software.
4) Managed Detailed measures of the software process and product quality are collected. Both the software process and products are quantitatively understood and controlled.
5) Optimizing Continuous process improvement is enabled by quantitative feedback from the process and from piloting innovative ideas and technologies.
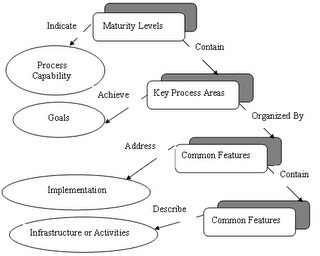
The structure of the Capability Maturity model is as shown below:
At the Optimizing Level or the CMM level5, the entire organization is focused on continuous Quantitative feedback from previous projects is used to improve the project management, usually using pilot projects, using the skills shown in level 4. The focus is on continuous process improvement.
Software project teams in SEI CMM Level 5 organizations analyze defects to determine their causes. Software processes are evaluated to prevent known types of defects from recurring, and lessons learned are disseminated to other projects. The software process capability of Level 5 organizations can be characterized as continuously improving because Level 5 organizations are continuously striving to improve the range of their process capability, thereby improving the process performance of their projects. Improvement occurs both by incremental advancements in the existing process and by innovations using new technologies and methods.Previously known as Key Process Area (KPA)
A process area (PA) contains the goals that must be reached in order to improve a software process. A PA is said to be satisfied when procedures are in place to reach the corresponding goals. A software organization has achieved a specific maturity level once all the corresponding PAs are satisfied. The process areas (PA's) have the following features:
1) Identify a cluster of related activities that, when performed collectively, achieve a set of goals considered important for enhancing process capability.2) Defined to reside at a single maturity level.
3) Identify the issues that must be addressed to achieve a maturity level.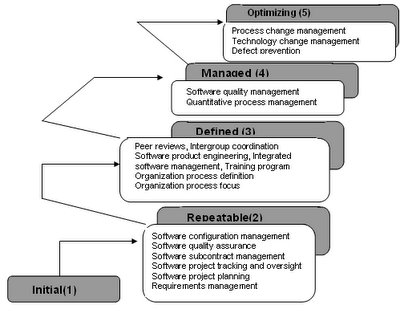
The different maturity levels have different process areas pre-defined as shown in the figure above. The SEI CMMI Level 5 has 3 PA's defined:
- Process change management: To identify the causes of defects and prevent them from recurring.
- Technology change management: To identify beneficial new technology and transfer them in an orderly manner
- Defect prevention: To continually improve the process to improve quality, increase productivity, and decrease development time.
The purpose of Process Change Management is to continually improve the software processes used in the organization with the intent of improving software quality, increasing productivity, and decreasing the cycle time for product development. When software process improvements are approved for normal practice, the organization's standard software process and the projects' defined software processes are revised as suited.
The goals sought to achieve are as follows:
- Continuous process improvement is planned.
- Participation in the organization's software process improvement activities is organization wide.
- The organization's standard software process and the projects defined software processes are improved continuously.
These defined standards give the organization a commitment to perform because:
- The organization follows a written policy for implementing software process improvements.
- Senior management sponsors the organization's activities for software process improvement.
The ability of the organization to perform transpires because:
- Adequate resources and funding are provided for software process improvement activities.
- Software managers receive required training in software process improvement.
- The managers and technical staff of the software engineering group and other software-related groups receive required training in software process improvement.
- Senior management receives required training in software process improvement.
Capability Maturity Model (CMM) Process Area (PA) Activities
The Process Area Activities performed include:
* A software process improvement program is established which empowers the members of the organization to improve the processes of the organization.
* The group responsible for the organization's software process activities coordinates the software process improvement activities.
* The organization develops and maintains a plan for software process improvement according to a documented procedure.
* The software process improvement activities are performed in accordance with the software process improvement plan.
* Software process improvement proposals are handled according to a documented procedure.
* Members of the organization actively participate in teams to develop software process improvements for assigned process areas.
* Where appropriate, the software process improvements are installed on a pilot basis to determine their benefits and effectiveness before they are introduced into normal practice.
* When the decision is made to transfer a software process improvement into normal practice, the improvement is implemented according to a documented procedure.
* Records of software process improvement activities are maintained.
* Software managers and technical staff receive feedback on the status and results of the software process improvement activities on an event-driven basis.
The primary purpose of periodic reviews by senior management is to provide awareness of, and insight into, software process activities at an appropriate level of abstraction and in a timely manner. The time between reviews should meet the needs of the organization and may be lengthy, as long as adequate mechanisms for exception reporting are available.
The Capability Maturity Model has been criticized in that, that it does not describe how to create an effective software development organization. The traits it measures are in practice very hard to develop in an organization, even though they are very easy to recognize. However, it cannot be denied that the Capability Maturity Model reliably assesses an organization's sophistication about software development.
The CMM was invented to give military officers a quick way to assess and describe contractors' abilities to provide correct software on time. It has been a roaring success in this role. So much so that it caused panic-stricken salespeople to clamor for their engineering organizations to "implement CMM" with CMM level 5 being the ultimate.


<< Home